WhitePaper
Whitepaper on the Future of Public Media
This is a space for collaborative writing and editing of a whitepaper on the Future of Public Media. We hope to present this Whitepaper to the new Corporation for Public Broadcasting committee on new media that will convene for the first time in the summer of 2008. Contributors so far: Ernest Wilson, Sasha Costanza-Chock, Wally Baer, Jessica Clark, Persephone Miel, Russ Newman, Jon Taplin.
A Note on Collaboration Tools
We began by using googledocs for drafting: http://docs.google.com/Doc?id=dcr23n54_37fd9w7
But we are shifting everything to this public wiki: http://cyber.law.harvard.edu/mediarepublicforum/WhitePaper.
We encourage people to help us gather relevant material from around the web using this shared tag: public.media. An example: http://del.icio.us/tag/public.media
There is also an existing 'Future of Public Media' wiki set up by center for social media, please review: http://futureofpublicmedia.wikispaces.com/
OUTLINE
Title: (placeholder: The Future of Public Media)
Abstract: One paragraph summary goes here.
Executive Summary summarize whitepaper and key recommendations in just a few pages. To do once whitepaper is finished.
I. Introduction overview, lays out broad contours of the field and what the whitepaper will do. Includes short section on history and goals of public media (Wally Baer will do the history section.)
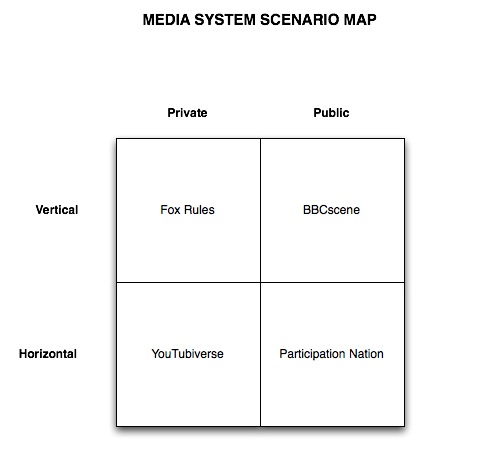
II. Futures Here we do a future mapping exercise with the two axes being: public/private, vertical/horizontal. This gets us four quadrants of potential media ecology futures to explore, public vertical (BBCscene), public horizontal (Participation Nation), private vertical (Fox rules), private horizontal (YouTubiverse). Describe the main features of each quadrant in a short paragraph. What would it look like, how will we know which world we're in, and what would be the consequences for our goals.
III. Maps Here we describe and map the current media ecology w/the various players and sectors. (Jessica?) Should include a section on Innovation at the edges: examples of best practice in new media, where we describe some of the good initiatives that are already underway in the public media sector, or those that have been proposed but not moving forward yet. This lays out what is happening in the 'horizontal/public' sector of our grid.
IV. Conclusions Here we summarize and suggest
- A. Principles for Public New Media
- B. Cross cutting factors
- C. Strategy for implementation. Includes the participatory carnegie commission idea: to generate public dialogue and move us toward the scenario we want.
Appendices
- Maps
- One-pagers (condensed versions of principles and recommendations)
- Checklists (checklists for review of applications / sites / public media experiments)
- Other appendices
Bibliography Or works cited.
I. INTRODUCTION
The end of the first decade of the 21st century is a time of radical transformation in local, regional, and global communication ecologies. In the commercial media sector, the traditional dominance of the US based cultural industries has on the one hand been extended through greater transnational penetration of distribution networks, while at the same time US cultural producers are challenged by the emergence of powerful competing regional cultural industries in India, China, South Korea, Nigeria, Brazil, and elsewhere. Simultaneously, the advance and diffusion of networked Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs) has radically transformed the media landscape both domestically and abroad. Commercial broadcast television, both entertainment and news, is losing viewership and advertising revenue as audiences fragment across the multichannel cable and satellite universe as well as the Net. Newspapers, which have served as the main employers of journalists and the primary producers of original investigative reporting for the last century, are in the midst of a crisis as both subscriptions and advertising revenue, especially classifieds, continue their steady decline.
Public media in the US, built on the broadcasting model (broadcast television and radio), faces challenges similar to those of commercial broadcasters: declining viewership and audience fragmentation, rapid technological change, shifting political climate.While National Public Radio (NPR) has been able to buck this trend and build a larger audience for its signature shows (Morning Edition and All Things Considered, PBS has seen its television audience decline significantly. Like commercial broadcasters, public media in the US must transform to engage the new communication environment of many-to-many communication, user generated content, audience participation, collaborative production and filtering, and peer-to-peer distribution. Younger people, especially, live in a media world centered on participatory communication platforms like MySpace, YouTube, and Wikipedia. At the same time, already marginalized groups of people face the threat of further marginalization when they lack access to the infrastructure, tools, and skills of the digital economy, including digital media. In short, like commercial broadcasters, if public media does not transform, it is in danger of becoming irrelevant, but with the added weight that a next generation public media system must be linked to successful ICT access and education policies in order to achieve its goals.
However, while there is danger, there is also great possibility. The widespread diffusion of the tools and skills of media production presents an opportunity for the public media system to engage with publics in ways never before possible. Public broadcasting continues to enjoy a level of trust unmatched by any of the commercial broadcasters. In an environment of information overload, this trusted status is one of the most crucial elements sought by online content providers. If leveraged correctly, this trust will help the public media system in the US undergo the transition to the new media ecology and strike the difficult balance between content producer, filter, and participatory platform for production and distribution. What's more, this is not uncharted territory. Public media can (and must) learn from and build on the successes and mistakes of other media firms, both 'new' media organizations that were born in the networked world of participatory content production and filtering practices, and 'old' media that are successfully making the transition. In addition Public media analysts must look to the differences in the Radio and TV production and distribution models in the U.S. that are producing such variant outcomes.
For example, one place for the US public broadcasters to look is at Ofcom, which has recently announced plans to fund public interest oriented new media through a 'public service publisher' program (http://www.ofcom.org.uk/media/news/2005/02/nr_20050208). Rethinking public media in the US should also draw from the lessons of both the commercial sector, including the so-called Web 2.0 firms, as well as nonprofit platforms built on Free and Open Source Software that are some of the most popular information sources today (like Wikipedia) or that contain some of the most interesting and valuable media resources (like Archive.org). It will also be key to figure out the link to locally grounded, face to face, geographic communities. For example, Wikinews is about to launch a pilot program (funded by the Knight Foundation) to create community media centers where community members learn media production skills for the online environment. Along these lines, the transformation of Public Access TV will also be part of the challenge, as cable companies seek to shift franchising agreements away from cities to the state or even federal level. Some Public Access stations, like Denver Open Media, have already developed radically innovative new models for participation and distribution (www.denveropenmedia.org). There is also an important opportunity to shift the balance of copyright back towards the public by changing the way publicly funded media content is licensed, for example through Creative Commons licensing.
This white paper on the future of public media is based on readings and interviews dealing with the history and current state of public media in the US, with attention to international developments, current proposals for public media innovation in the new media landscape, and examination of already existing 'new public media' pilot projects.
[To rewrite: The structure of this white paper includes: a review of the current and
near future media landscape; review of existing public media
institutions; review of new media innovations in commercial, nonprofit,
and community media sectors, with a focus on innovations that can be
adapted to the goals of public media; a review of the necessary enabling
environment for 'new public media' programs to be successful; a
discussion of evaluation mechanisms.]
II. FUTURES
Here we do a future mapping exercise with the two axes being: public/private, vertical/horizontal. This gets us four quadrants of potential media ecology futures to explore, public vertical (BBCscene), public horizontal (Participation Nation), private vertical (Fox rules), private horizontal (YouTubiverse). This section describes the implications of each scenario, the perceived trend (where we think we are heading), which should we hope for, and how do we get there.
III. MAPS
Here we describe and map the current media ecology w/the various players and sectors. (Jessica?) Should include a section on Innovation at the edges: examples of best practice in new media, where we describe some of the good initiatives that are already underway in the public media sector, or those that have been proposed but not moving forward yet. This lays out what is happening in the 'horizontal/public' sector of our grid.
IV. CONCLUSIONS
PRINCIPLES OF PUBLIC NEW MEDIA
1. Horizontal
(Distributed, Bottom-up). The great thing about new media is that the tools of production are radically decentralized; people all over the country are now producing a torrent of amazing stuff with consumer grade videocams and home computers. The challenge is for CPB to find good mechanism to create a 'pipeline' where the best content filters up, meaning receives broader distribution cross platform. The ideal model, to me? Local editorial board in each city/area, with good representation of the community (maybe elected?) selects a combination of most popular (most views/best rated) content, with editors discretion to promote non-popular but socially important content, and these 'best of' selects get aired on local TV affiliate plus (potentially) bumped up to national distribution. There are some existing models for this, although none has been fully resourced/implemented well. Current TV has elements, as does Indymedia.
2. Open
- Content: freely viewable, freely downloadable, available for remix and reuse, preferably creative commons licensed.
- Format: open (nonproprietary) format.
- Infrastructure: based as much as possible on free/libre open source software (FLOSS).
3. Multimodal
'New Media' doesn't just mean internet. The CPB should build the idea of cross platform media into whatever it does in this area, with an understanding that new platforms continue to evolve at an ever increasing rate. Internet, mobile phones, iPods, multiplayer games, virtual worlds, geolocative media... the CPB new media should recognize from the start a multimodal media universe and plan to support and strengthen media that promotes the goals of CPB regardless of platform(s) and cross platforms. Narratives and content elements in commercial media are increasingly reused and spread across several platforms, public media should do this too.
Cross-Cutting themes
A. Access
people in the US suffer severe access inequality to new media tools and skills along lines of race, class, gender, and geography. For one thing, we need much better data on communication access inequality. But we know enough to recognize that just making an 'open' publishing system ('anyone can post their media here') will reproduce the existing access inequality. So, there must be mechanisms to actively seek out and promote content producers who can represent and speak to the widest range of diversity of the American experience. Otherwise, the voices of new public media will be the same voices that dominate the old public media: middle class white dudes.
B. Best Practice
There are already great examples of how to integrate new media on the margins of public media system. Denver Open Access is a great example. (get at least 3 good examples).
C. Cross-platform.
We need to figure out the best arrangement to allow public media content to get to the user across all platforms. Currently, one of the biggest challenges is to get public media onto all mobile devices. This can range from consensual agreements with the private sector to carry public media and provide it free of cost (for example, arrange with Verizon to carry public media video clips as a free content service for all video-enabled mobile phone subscribers), to a 'mobile must-carry:' if you want to be a wireless service provider, you have to carry public media content and make it a freely available 'channel' for your subscribers. It could be done city by city (like public access clauses in cable franchise agreements) or (more likely) at the state or federal level.
This gets complicated, in part the problem is solved if we can successfully get 'network neutrality' on mobile data service providers (the subscriber can then access 'whatever content they want'). In practice, though, the way the mobile providers are rolling out video is a walled garden model, with preselected available 'channels' at a top-level menu for the user. Public New Media needs to be in that top-level menu. Ideally this can be pitched as a 'win-win' to the service providers: they get free content to offer their subscribers, public media gets free distribution to mobile devices, and the public gets free access to public media via their mobile devices.
Strategies
How do we get from here to there?
- Expert views: whitepapers
- Public views: participatory Carnegie Commission
- Focal points for public pressure? Example - CPB focal point: new media committee
- Legislation?
APPENDIX: BEST PRACTICES FOR PUBLIC DIGITAL MEDIA DISTRO SITE CHECKLIST:
- content freely available, or pay for content model?
- If ad revenues involved, is there revenue sharing? How does it work?
- open content licensing system?
- easy to embed content in other pages?
- easy to download content?
- download content in high-quality format for remix?
- will provider fight takedowns?
- anonymous publishing when necessary?
- FOSS?
- role of the community:
- comments?
- ratings?
- tags?
- degree of editorial power?
- thought of as producers?
- remix?
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Anderson, Simon P. and Coate, Stephen. 2000. "Market Provision of Public Goods: The Case of Broadcasting" (January 2000). NBER Working Paper Series, Vol. w7513. Available at SSRN: http://ssrn.com/abstract=217909
Aufderhelde, Patricia. Public Television and the Public Sphere. 1991. Critical Studies in Mass Communication; Jun91, Vol. 8 Issue 2, p168, 16p.
D Atkinson, M Raboy. 1997. Public service broadcasting: the challenges of the twenty-first century. UNESCO.
Avery, RK. 1993. Public Service Broadcasting in a Multichannel Environment: The History and Survival of an Ideal.
P Bélanger. 2004. Public Broadcasting and the Public Interest. Canadian Journal of Communication.
Benkler, Yochai. The Wealth of Networks.
Jay G. Blumler, Wolfgang Hoffmann-Riem (1992) New Roles for Public Television in Western Europe: Challenges and Prospects. Journal of Communication 42 (1), 20â35.
M Comrie, S Fountaine 2005. Retrieving public service broadcasting: treading a fine line at TVNZ. Media, Culture & Society.
Clark, Jessica. 2007. "Big Dreams, small screens: Online Video for Public Knowledge and Action. A Future of Public Media Project. Center for Social Media, American University School of Communication.
Dornfeld, Barry. Producing Public Television, Producing Public Culture.
Engleman, R. "Public Radio and Television in America: A Political History." JOURNALISM AND MASS COMMUNICATION QUARTERLY, 1997, VOL 74; NUMBER 1.
Gregory, Sam and Witness. 2005. Video for change : a guide for advocacy and activism. London ; Ann Arbor MI: Pluto Press.
Halleck, DeeDee. 2002. Hand-held visions : the impossible possibilities of community media. New York: Fordham University Press.
Holtz-Bacha, Christina, and Norris, P. 2001. Political Communication; Apr-Jun2001, Vol. 18 Issue 2, p123-140.
Howley, Kevin. 2004. "Remaking public service broadcasting: lessons from Allston-Brighton free radio." Social Movement Studies 3:221-240.
Hoynes, William. 1994. Public television for sale : media, the market, and the public sphere. Boulder, Colo. : Westview Press.
Norris, P. 2004. Public broadcasting in the digital age: Issues for television in New Zealand.
JO'Hagan, M Jennings. 2003. Public Broadcasting in Europe: Rationale, Licence Fee and Other Issues. Journal of Cultural Economics, 2003
Peacock, A, D Graham. 2004. Public Service Broadcasting Without the BBC? papers.ssrn.com
ME Price, M Raboy. 2003. Public service broadcasting in transition: a documentary reader. Kluwer Law International
Raboy, M. 1995. Public Broadcasting for the 21st Century. University of Luton Press Luton, Bedfordshire, England.
Rodriguez, Clemencia. 2001. Fissures in the Mediascape: An International Study of Citizensâ Media. Newbury Park: Hampton Press.
Jerry Star [citizens for independent public broadcasting - wrote a book on creating a $1 Billion fund for public broadcasting to free it from political manipulation]
George Tsourvakas. (2004) Public Television Programming Strategy Before and After Competition: The Greek Case. Journal of Media Economics 17:3, 193
Ward, D. 2004. Public Service Broadcasting: Change and Continuity.
NOTES
Review these notes, incorporate into text where needed.
RECOMMENDATIONS
Decentralized distributed process of discussion on the future of public broadcasting. House Party model pioneered by MoveOn? A network of public hearings with 4 bigger ones as anchors? A series of whitepapers: one by existing CPB people, one by outside 'experts', another by the Public, and then draw from all of them? etc.
NOTE: "Public Media should be Open Media" CMS, Codecs, standards, players, and other tools should as far as possible be FOSS. Licensing should as far as possible be Public Domain and/or Creative Commons [Attribution-(non?)Commercial-(Sharealike?)]
PLAYERS
Station Resource Group NPR PBS APM - American Public Media PRI (cable access stations?) (LPFM stations?)
A-REPS (The NPR Authorized Representatives) IMA SRG (Station Resource Group)
Digital Distribution Task Force (?)
PRECEDENTS
Digital Distribution Consortium Public Radio Exchange Public Service Publisher NPR-station podcasting partnership NBBC (video aggregation) Public Interactive ContentDepot
- vendors and service providers:
The Platform BrightCove Internet Online Distribution Alliance
LINKS
http://digitaldistribution.wikispaces.com/
CPB, PBS, Blinkx.com (?), NPR, PRI, APM (American Public Media), SRG (Station Resources Group), DDC (Digital
Distribution Consortium), PRX (Public Radio Exchange), and PI (Public Interactive).
Ford Foundation Future of Public Media initiative. See grantees list: http://www.centerforsocialmedia.org/blogs/future_of_public_media/dec07fordupdates/
Integrated Media Association: http://integratedmedia.org
Center for Social Media at American University
Berkman Center
Minnesota Public Radio
Denver Open Media
NPR retraining journalists
Jake Shapiro (PRX)
Michael Kleeman (Digital Futures Initiative)
Archive.org: http://archive.org
Beyond Broadcast: http://www.beyondbroadcast.net
Buzz Machine post on 'exploding public media:' http://www.buzzmachine.com/2006/07/24/exploding-public-media/
Center for Social Media Future of Public Media blog: http://www.centerforsocialmedia.org/blogs/future_of_public_media/
and wiki: http://futureofpublicmedia.wikispaces.com/
Creative Commons: http://creativecommons.org
Denver Open Media: http://www.denveropenmedia.org
Manhattan Neighborhood Network: http://mnn.org
NewAssignment.net
Ofcom's 'public service publisher' program (http://www.ofcom.org.uk/media/news/2005/02/nr_20050208)
Wikinews: http://wikinews.org
steve monteel: center for justice and journalism
Need to talk to Michael Parks, just came back from BBC meeting and European pubcasting
Ford Foundation has been holding meetings on 'democratic voices in global online communities'
Orland Bagwell: Ford program officer who is doing this stuff.
Peter Schwartz
Renew Media/Reframe: http://radar.oreilly.com/archives/2007/08/reframe_moving.html
OMN, but Whither OMN now that founder/funder Mike Homer is, sadly, passing away:
http://sanfrancisco.bizjournals.com/sanfrancisco/stories/2007/08/27/story1.html
Miro: (formerly Democracy Player, recently got $ from Surnda Foundation as well as Mozilla):
http://www.getmiro.com
Conversations Network. Jake Shapiro is on the board of this nonprofit, could play a role in a new architecture for public radio:http://radar.oreilly.com/archives/2007/08/reframe_moving.html
Public Interactive. Sits in a key spot in the emerging digital public media space but needs reinvigorating/focus:
http://www.publicinteractive.com/
NPR and WGBH combine to create new advertising/underwriting sales company:
Official news: http://www.npr.org/about/press/2007/091107.npb.html
Staci has a good line on it at the end of her blurb: http://www.paidcontent.org/entry/419-npr-wgbh-to-acquire-sponsorship-rep-national-public-broadcasting/
American Archive project I was telling you about, here are some background links:
http://www.current.org/dtv/dtv0708preservation.shtml
http://www.cpb.org/grants/grant.php?id=104
http://www.current.org/federal/fed0702apts.shtml
More about 'My Source.'
Need to research One Economy: one-economy.com. nonprofit that does technology and poverty work. support from McCain and Obama. 'Public Internet Channel.'
--
Wally: I also like your idea in 5. of a four quadrant mapping -- public/private, vertical/horizontal -- but it seems to me this should start in 3., or maybe earlier, with a mapping of existing stakeholders. Presumably this will show that 1) economic and political power still resides largely in the vertical sector, both public and private; 2) there's lots going on in the horizontal/private sector; and 3) the horizontal/public sector is still relatively underdeveloped.
I assume that you intend "public" to include both government and nonprofit organizations.
The next section (your 4.) then focuses on what's happening in the horizontal/public sector, leading to a discussion (your 5.) of how media in general, and public media in particular, may evolve within and between the four quadrants. I'd expect to see substantial movement from vertical to horizontal, and less of a bright line between horizontal public and private as more hybrids and partnerships form. But you may have different scenarios, and I look forward to discussing all this with you.
I agree that the conclusions/next steps (6.) should focus on building a participatory dialog process which would complement Ernie's proposal to Carnegie, but would be worth doing in any event.
One dimension not covered in the four quadrants is content/conduit, which is now largely but not entirely bundled in the vertical sectors, and unbundled in the horizontal sectors. That may imply that distribution in a p2p world becomes less critical for the future of public media, but somebody -- public or private -- has to build and operate the underlying distribution networks.
We should include international examples that serve as models or provide lessons learned for public media evolution toward the horizontal sector. Certainly the BBC's initiatives and Ofcom's PSP, but also the examples from Korea that you've spoken of, and others that you think are relevant.
For section 2, I'll include CPB, PBS, Blinkx.com (?), NPR, PRI, APM (American Public Media), SRG (Station Resources Group), DDC (Digital Distribution Consortium), PRX (Public Radio Exchange), and PI (Public Interactive). These are primarily vertical entities. Are there others, particularly public horizontal entities, that exist now and should be included?
KCRW as a case study
Worry about the 'death' public broadcasting
'Connect the best of the bubbling stew of new media to the institutions of public media'
best practices in public media
Propose the participatory 'new carnegie commission'
- who would manage it?
- internationalize the conversation
- do a korea case study
--
Notes from Online News Managers talk Oct 3 2007
'It's a conversation, stupid' wikis, blogs, social networking and mainstream journalism
- The LA Times wikitorial debacle (but they didn't talk to anyone about how to actually do a wiki). - Seattle Post Intelligencer talk. UGC is now fully integrated into what they do.
-CNN (basically saying that they need to embrace participatory journalism. "I reporter" project. Showed clips from CNN i report (their logo even looks like an indymedia logo) from Burma.
- Yahoo news. They recently took down most of their message boards. They are focusing on the 2008 elections. Pulling in Flickr, using Yahoo Answers, Groups, MyBlogLog.
- Kinsey Wilson took down message boards in 2003-4 because people were making threats against th president.
- Newsvine.com.
Question: re: collective licensing. revenue sharing.
Public Media question
- Minessota public media isn't really engaging the community. They are sending out surveys. Some other stations might be doing better stuff.
- One problem of public radio is that the reason for the existence of the public media is in question. Perhaps social media replaces public media.
- NPR: developing a new mobile service. Local numbers that people can call to hear local stories. Trying lots of different avenues. Some of NPR online has been held back by the desires of local NPR stations.
- Supports NPR podcasts. Would like to donate to the local producers.
portability
- Shouldn't have to go to the site to get the content you want to get. People are consuming content via RSS. But how do you monetize content? It's easy to monetize content on sites. There are CPMs. But what about viewing content on someone else's site? In an email? In an RSS reader?
2/3 of viewers aren't coming through their sites.
diversity
- panel is 4 white men and 2 white women. - online news doesn't reflect diverse communities any more than traditional media does. - language diversity - be sure that you take content via cell phones
--
- Consider various scenarios of what the communication ecology might look like. For example: 2 axes: public <----> private / horizontal <---> vertical (consider alternative axes to map things on)
Include the various actors and relationship to public media: Mass Media (PSAs and fairness doctrine) Web 2.0 (net neutrality, access, required or suggested 'feature' PSAs?) 'Public Minded' Entrepreneurs (Current.tv, IWTV) Big Pubcasters (PBS, NPR) Little Public Media (LPFM, Cable Access) Public institutions (Schools, Libraries, Museums, Archives) Youth Media Indymedia Spanish language press / public spanish language media? etc. Map all these, relationships
-- NOTES ON DDC PAPER
The Digital Distribution Consortium (DDC) Overview
DDC overview notes
A working group to discuss the future of NPR. Created a business plan. Bracketed issues of "governance, ownership, and the role of existing investments and infrastructure" in order to arrive at common ground.
p. 6: âcreate once, publish everywhereâ (COPE)
- revenue sharing (good! keep this).
- creative commons? - User generated content role? Motions towards bringing in new producers but not spelled out much. But also, they are doing 'b2b' backend. hmmm.
p. 7 Sales and Business Development - they are thinking primarily of major national sponsors. Do they consider possibilities for localizing sponsorship and sales? geolocative sponsorship. 'dynamic' sponsorship inserts based on user location? etc.
NOTE: "Geolocal sponsorship"
p 8: how about deals with as many mobile providers as possible to get free DDC content via mobile (where users currently have to pay for most commercial content).
[NOTE: they do mention "There is also the potential for presenters to insert local underwriting and/or station branding into the content itself â a system that poses technical and business challenges but provides an opportunity for stations to leverage local underwriting relationships across the content, more directly support station memberships and audience loyalty, and create new revenue." Take the local underwriting idea further.]
NOTE: "Mobile Must Carry" [? Perhaps not necessary if open mobile / neutral platform. And Simon says Dead on Arrival. But still useful to think about this question: how to get commercial mobile carriers to provide featured spots in menus, etc. to public interest media.] At a minimum this means content menu listing spot. Ideally also means actually carry/serve the content to mobile users for free.
-emphasis on free and open access to content is good
- FOSS platform? - open codecs?
NOTE: "Public Media should be Open Media" CMS, Codecs, standards, players, and other tools should as far as possible be FOSS. Licensing should as far as possible be Public Domain and/or Creative Commons [Attribution-(non?)Commercial-(Sharealike?)]
- does it make sense to build the thing tailored to audio content, or make it video as well from the start? how about photos?
- what is the relationship to the National Archive? To Archive.org?
- shouldn't platform and codecs sync across as many government media archives as possible? (NPR, PBS, National Archives, Museums, Libraries, Schools, etc?)
- Doesn't have to be (or make sense to be) the SAME archive. But should coordinate on standards & metadata. And standards should be free and open.
Governance? (board(s), hierarchy, who reports to who) Accountability? (community board(s)?) Ownership? (public, private, mixed, etc)
Random ideas
- can we get net neutrality into WTO/GATS telecom chapter?