Presentation
Hello - we are Amanda, Bruno, Franny, Hector and Yosuke of the Cyberlaw: Difficult Problems course. Feedback from people who use and are familiar with Wikipedia/Wikimedia is an extremely important part of formulating our proposed solution, and we thank you for your interest and contributions. We only ask that you direct your comments and input to the other Future of Wikipedia pages, and allow us to use this Presentation page to create our final class presentation. We look forward to hearing from you!
Introduction
It might border on banality for us to repeat many of the important criticisms of Wikipedia (and indeed some of the less important criticisms). Nevertheless, we here try to sketch out areas of concern, and in some parts, our rational for not so pursuing. Several sources provided us with different categories and examples of Wikipedia's criticisms: JZ's book, Wikimedia's Usability Initiative, Wikipedia's Village Pump, the Policies and guidelines (which implicitly draw attention to the small and large frictions that can develop within the community), the enthusiastic critique from commentary such as the Wikipedia Review, and in the spirit of user generated content and mass public distribution, YouTube videos. [Warning: contains mild profanity.]
Picking Our Battles
On God-Kings and Governance
Problems along this vein include:
- The odd status and power of Jimbo Wales, a "God-king who may or may not be able to act unilaterally" (JZ 141)
- The reliance on consensus, not on democracy
- The curious nature of a highly developed collaborative project, which has very wonderfully developed a governance structure and a form of constitutionalism. The level of development, however, can be a hindrance to reform, given the Wikipedians' strong devotion to the project and once more the need for consensus.
For purposes of the project, our group decided that we weren't about to kick out Jimmy, and the Wikipedians themselves as well as other media do a decent job at pointing out his previous controversies. Furthermore, the open and consensus-based nature of the Wikipedia project has resulted in very strong and thoughtful (though at times idiosyncratic) arrangements such as the Five Pillars that guide the activity of the encyclopedia. How can we ride on the strengths of such internal machinery while injecting new sources of strength? We believe that the strength, vibrancy, and growth of the Wikipedia community could bring new avenues of improvement.
Contradictory Missions?
This broad, rather generative project was kick-started with an outrageous idea and clever new (for 2001) web-publishing software. Other than a few key initial nudges (as well as the code behind the structure), the community was left to fill in the gaps on its own. Some of the resulting kinks include:
- The Inclusionism vs. Deletionism debate
- An interpretation of the banner project as an attempt to compile An Online Encyclopedia or The Sum of All Human Knowledge
- The stark differences in the vision and execution in the different language Wikipedias. (Compare the English and German sites)
Much has been written regarding the inclusionism/deletionism debate, from the popular media to the depths of obscure Wikipedia discussion pages. As strongly as some of us (Hector) may feel one way or the other (why exclude valuable information about minor Star Wars characters?!) about the matter, adding another voice to the shouting match would probably not settle most of the disagreements.
Quality
Our visiting friends from the Wikipedia Review were quite keen to correctly point out the differences between perceived and actual accuracy within Wikipedia. And indeed, different challenges are at hand in allaying the different concerns of different readers, who might be using Wikipedia to
- study for a med school exam,
- learn more about their Senator,
- write a 6th grade history paper, or
- write an Associated Press fluff piece about quality concerns in Wikipedia.
Currently, the most powerful tool in Wikipedia's arsenal against vandalism and inaccuracy is its editing base and the large number of eyeballs the community provides. Once again, the health and growth of the Wikipedia community are vital factors, as are the current policies regarding sources, references, and neutrality. We think that good solutions can tap into the project's very strengths here.
Issues in Education
When schools and colleges express concern over their students using or possibly misusing Wikipedia in their academic work, Wikipedia's own response has generally taken the mildly surprising form of acknowledging its limitations and underlining its proper use as a teriary source. Even so, this tertiary source is one that dominates many a student's initial research paths and quite often ends up being the only source consulted.
Another manner of addressing this problem can be to engage the students to collaborate with the Wikipedia project themselves. In doing so, they might learn more about an assigned topic (given the increasingly stringent requirements of relevance and citation within Wikipedia), learn more about collaborative projects more generally (with the rules, benefits, and pratfalls of such a subculture), all the while helping with Wikipedia's overall aims of further compiling human knowledge.
Various articles and even Wikipedia pages document how others have scratched at this possibility. While our own group's proposal is not directly about classroom participation in the Wikipedia community, we think that our concerns with streamlining certain forms of community participation could easily be ported towards more specific pedagogical implementations.
Identity and Growth of the Contributing Community
Size
Readers, Casual Editors, and Experienced Editors
Subcultural Aspects
Financial Sustainability?
Honing In
Interaction with the Community-Centric Nature of Wikipedia
- As it stands, Wikipedia does have a constitution, albeit a bit more like England's constitution
- What improvements could be consistent with Wikipedia's strengths, while providing forward-thinking alternatives?
- A choice to work within the hilarious environment that is a consensus-driven open collaboration
Regarding Deliverability
- Considering the reams of electronic text that have been written on the topic, we decided that a simple, actually implementable solution might fare better
- Wikipedia is quite open and quite dynamic. But one does get a sense that the experienced editors rule, with added clout stemming from knowing the levers and style of the community.
- Can we suggest a perspective or solution that can dovetail with the aims of the present and future Wikipedia community?
Selected Key Problems to Address
[Yosuke to expand]
- 1. Quality and reliability of content (e.g. factual errors on Wikipedia lowers the reliability and credibility of its content)
- 2. Wikipedia's editor base is decreasing (existing editors are losing interest and it is difficult to recruit new editors)
- 2.1 Deals with issues of:
- - community
- - motivations
- - outreach and public relations
- 2.1 Deals with issues of:
Different Perspectives on the Key Problems
[Bruno and Franny to expand]
- Bridgespan
- - think of Wikipedia as a movement in addition to a non-profit organization under the direction of a board
- Wikimedia
- Wikimedia Usability Initiative
- Wikipedia Review
- General public (primarily outside of Wikipedia editor community)
- CONTENT:
- 1. Too many people are writing/editing the same article.
- 2. Limit the number of people who can work on one article at any given time, and lock down good articles that shouldn't be changed, or only give access to writers/editors that are trusted.
- 1. Some of the information presented is false.
- 2. A suggestion is to make the material go through a process where it is checked by individuals before it is posted.
- 1. A lot of the information is false or inaccurate.
- 2. Have editors that check information before it is published.
- 1. it is not considered a reliable source by educators
- 2. prove that the information is reliable so students will be able to use it for academic reasons
- 1. The biggest problem with Wikipedia is that not all of the information is legitimate. Wikipedia is not a good source for papers and some of the information is false. Anyone can post information there.
- 2. You can solve the problem by having a team collaborate on user's information before it is posted.
- 1. The biggest problem is its trustworthyness. I'm never sure that I can trust the information on wikipeida.
- 2. This can be fixed by being more careful about putting in citations.
- 1. I think Wikipedia's lack of total credibility is its biggest problem. Many entries lack citations verifying the accuracy.
- 2. I think the problem can be solved by finding editors to check the accuracy of the entries made by people.
- 1. I think too many big information on a given topic. Information that is unnecessary for a common man.
- 2. Wikipedia can be made short perhaps a link for "advanced reading" given seperately and only the basic information in the main page.
- 1. The grammar and sentence structure is often wrong or confusing.
- 2. Use grammar check and make people edit the texts.
- 1. The biggest problem is some of it is more opinion than fact.
- 2. A way to solve this is just to have the writer mention facts, and not on opinion or speculation.
- 1: The biggest problem is that most of the articles lack references and professionalism.
- 2: One solution is not to allow just any user to edit or create an article with providing good and "quality" references first, and then having a professional to look over the article and make sure it meets high quality standards before being published.
- 1. I think the biggest problem with the current Wikipedia is that quite a few things, such as medical terms or conditions, are either not even listed or only have a very, very basic explanation.
- 2. I think you can solve those problems by working on collecting & posting more detailed information about topics you only have a brief description of or that there is currently no information about on the site.
- 1. non expert opinion of explanation about subjects which looks like an expert explanation.
- 2. just do a simple test before letting people to post articals
- 1. I believe there is some inconsistency in the correct knowledge about topics.
- 2. This could be changed by having more experts on topics reviewing the information before it is posted.
- 1. I think the biggest problem is that anybody can submit information, and there is no real way to verify if the information is even correct or not.
- 2. Wikipedia needs to start really investigating who is submitting information and makes sure that correct information isn't tampered with.
- 1. In many articles recent updations are not clear in wiki.Sometimes wrong informations are given or outdated informations.
- 2. Make a team for checking the article ,they can create updations if needed.
- 1. Not peer reviewed.
- 2. Have professionals review articles before posted.
- 1. Extreme left wing bias, as well as failure to monitor those who have extreme bias. The Climategate scientist who edited hundreds of articles in Wikipedia and wiped out all mention of the Medieval Warm Period and anything that included discussion of other causes of global warming (such as solar activity or continuation of human deforestation as agriculture advanced) were removed.
- 2. Allow those who report slander and abuse to have the editor's changes removed. Allow those who have credentials in their field to have a higher value in their edits than general off the street users.
- 1. People write things that aren't correct or accurate on Wikipedia.
- 2. To solve the problem, Wikipedia can hire professionals to verify all information posted on Wikipedia.
- 1. Unverified informatioin.
- 2. Require the production of the reference to support the information's accuracy.
- 1. There is no standard level education or research ability to those who edit it.
- 2. Allow only those who can provide necessary abilities and pass tests and reviews by wikipedia standards.
- 1: GIVING THE UNWANTED MORE INFORMATION TRY TO REDUCE THE INFORMATION
- 2: SHORT THE STORIES INTO THE IMPORTANT LINES ONLY WHICH CAN HELPS US TO SEE THE MAIN POINTS
- 1. The biggest problem with Wikipedia is also its greatest strength - its inclusivity in that anyone can amend add information. A lot of people think that, therefore, the information on the site may not necessarily be accurate, and may even be deliberately misleading. For example : dates of death given for people who are still alive.
- 2. All information should be centrally vetted for accurate content. This should be highly publicized.
- 1. The length of the content, the huge history sections and irrelevant information.
- 2. Cut back on the history and the unneeded text sections, paraphrase.
- 1. Wikipedia describes every concept in a detailed manner; sometimes it is so deep that is confusing to layman.
- 2. This problem could be solved by adding pictorial representation of the data and also by using simple words and sentences.
- 1. Not articles on every person subject
- 2. Not everyone will write articles. Let people suggest articles that should be added, then hire people to write articles on the suggested subjects.
- 1. Anyone can edit the information so the content is unreliable.
- 2. Have a screening procedure by which people have to sign up, state credentials and a method of verifying them and be given a password in order to change or add information.
- 1. Wikipedia lacks in depth articles. Only the basics are available in many cases.
- 2. Could you link it with Google search's database somehow to get the specific result ?
- 1. Incorrect information
- 2. Restrict editing to qualified professionals in that field
- VANDALISM AND ATTRIBUTION:
- 1. The biggest problem is people can use anonymity to vandalize Wikipedia in both blatant and sneaky ways.
- 2. The best way to solve the problem is to ban anonymous edits and require a verified email address. This preserves the fundamental principle of allowing anyone to edit because anyone can get a free yahoo or hotmail account and use it to register. But it will deter a lot of the vandalism because signing up for a free email account and then registering a Wiki account is more trouble than it's worth if your intent is to vandalize (and get banned quickly). But if you want to make legitimate contributions, going through the process one time is only a minor inconvenience.
- 1. People vandalising pages or putting unsourced information.
- 2. Only allowing trusted members to add content or edit information on wikipedia's pages
- 1. The ability for someone on a local computer to mess around and change words on the site.
- 2. Make the user register to post comments instead of just letting them post it. As for as myself concerned Wikipedia is on the right path and if somebody feels any hardship it will gradually be eliminated.
- 1. Sometimes you cannot trust the person who gives the information it provides.
- 2. The solution here is to have a background of the person who gave the information in Wikipedia.
- 1. People putting in information that is not correct, when they know it's not correct, but because they think it's funny/amusing.
- 2. Require information be checked by a second person before it's put into an article.
- 1. The biggest problem with Wikipedia is that anyone can edit it.
- 2. I think that those who edit the information on the site should have some sort of qualification and it should be subject to review before being displayed.
- 1. Wikipedia is open to have their definitions being changed and there have been charges that some of the definitions have been hacked and manipulated by people that want to have their version of an event validated on Wikipedia.
- 2. The solution might be to have a review panel to look over disputed items or complaints to see if the definition is valid.
- 1. Too much vandalism and unreliability of information.
- 2. Allow only registered members to edit/create pages. Make sure those registered members are confirmed through CAPTCHA, email, etc. And have more experienced moderators assigned to different categories to check page edits.
- SEARCH AND TECHNICAL INFRASTRUCTURE:
- 1. The biggest problem with Wikipedia is not being able to find the meanings to an given subject.
- 2. The solution is to make details more simpler for others to understand so that it will be easier for users to find the answers that they are seeking.
- 1. The main problem is answers are scattered.
- 2. By ordering it we can solve it.
- 1. Using javascript (extensions/UsabilityInitiative/*) causes certain browsers (Mozilla 1.7) to crash.
- 2. Re-write scripts so that they work.
- 1. in my point of view all the answers given by the Wikipedia is perfect. but the arrangement of all answers is not attractive.
- 2. for avoid this problem please make some attraction back round and tabulation usage also must. thank you.
- 1. if we try to search anything in wikipedia means its taking much longer time to load the page than othersites.
- 2. you can increase the bandwidth of the site,thus making it a fast one
- 1. The problem is we need seperate search Engine for all fields.
- 2. plz create an search Engine about all the fields.
- 1: In terms of search pages, if doesn`t find any match it is not even bringing any related topics to its users.
- 2: In cases of not finding any match for search result, it can atleast mention linked search result thru someother search websites.
- 1. PAGE LOADING TAKING LOT OF TIME IN WIKIPEDIA when compared to Google.
- 2. Please make the site in such a way that page loads quickly
- GOVERNANCE:
- 1. Wikilawyering is the most frustrating part of working on Wikipedia. A casual user like me is easily intimated when more experienced members invoke seemingly obscure Wikipedia policies.
- 2. Simplify and reduce the number of Wikipedia policy pages.
- MISCELLANEOUS:
- 1. Funding
- 2. Offer a premium upgrade with fuller content, additional resources (eb.com, hoovers.com, amazon.com, bankrate.com, *.edu, *.gov, *.org), integrated video with real-time RSS and twitter feeds. Set the price at something low to entice those who want the upgrade as easy as saying "yes". I recommend no more than $1.99/month * 1,000,000 users the first month = $1,990,000. This would alleviate Jimmy from having to beg 3 times a year for help and would immensely improve the quality of the information. mechturk@ymail.com
- 1. Global warming is the biggest problem of current Wikipedia.
- 2. It can be solve by growing more trees
- I could not find any problem on Wikipedia. Many times, i am read Wikipedia frequently.
- There is absolutely nothing wrong with Wikipedia! Please donot try to "fix" something that is not broken!!!
Analysis
[Bruno and Franny to expand]
- Must reach out to user base outside of Wikipedia's community; How does that user base perceive Wikipedia and its problems?
- What demographic are we reaching out to? how will we reach that demographic?
- Utilizing crowdsourcing techniques to highlight factual inaccuracies? How can we harness voluntary contributory energies?
- Organization and filtering techniques will make it easier to match factual inaccuracies with editors (new or existing) willing and able to make corrections
Proposed Solutions
[Amanda to expand]
- Changing the production system from a decentralized to a semi-centralized one in respect to what would be considered an article approved for publication by Wikipedia. The aim would be to develop a culture of developing different versions of articles that are preceded by a beta versions before their official launch. Most of this is inspired by software production system.
- Develop an outreach campaign focused at both increasing Wikipedia's user base and improving the quality of user participation (e.g. Donate edits to Wikipedia)
- Discuss promotional campaign to launch application
- Filtering/sorting mechanisms for the landing page - perhaps link to a re-organized Community Portal page
- Link landing page to a web initiative similar to Aardvark
- Integration with banner and other promotional tools on Wikipedia pages
- Strengthening relationship and partnering with secondary school systems (e.g. lesson plan proposal)
- Create a GreasyMonkey script for the purposes of:
- - highlighting incorrect/disputed/highly disputed information and creating an accessible database issues;
- - reaching out to readers of Wikipedia and drawing them into the Wikipedia editor community.
PRODUCT SPEC:
Wikipedia Educational Browser Extension
WRITTEN DESCRIPTION:
This browser extension serves many purposes: first, it is meant to facilitate the identification of factual errors within Wikipedia by creating a user-friendly way to catalog the errors using Wikipedia's taxonomy - which you can find under the open task bar in this link <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Community_portal>, second, it provides an inroad for new potential editors to interact with the site through micro-contributions and build familiarity with Wikipedia process, third it teaches users to do not completely rely on the text he/she is reading and to point him/her to which areas need contribution [?], fourth, it would also work as a way to bring the discussion page to the surface, teaching them to "discuss before editing".
What to Build (Description) â please forgive the non-technical nature of this spec. We are happy to provide additional information including more views if needed.
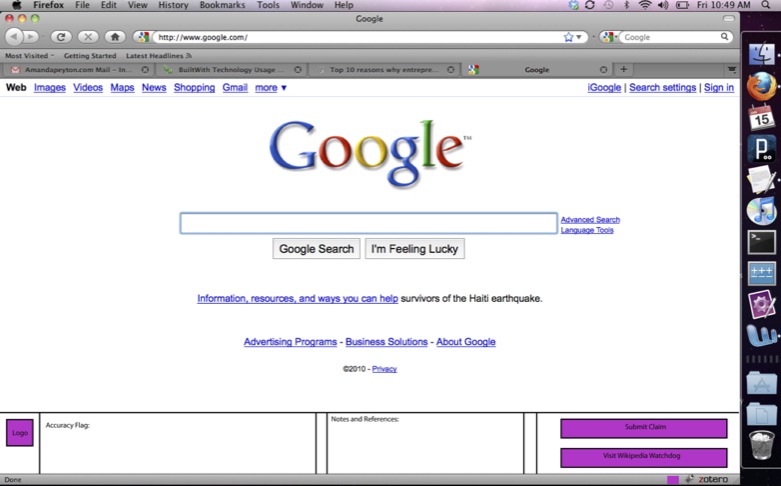
After the user installs the plugin, there should be a logo in the bottom right corner of the browser and an entry added to the âtoolsâ bar of the browser.
We imagine the interaction as follows:
When the user spots an error, he or she can click on our logo in the corner of the browser or click the entry in the Tools menu and a small window will pop up from the bottom of the browser (see below image for basic window design). Then, he or she would highlight the text that contains what the users suspects to be an error. The text would be auto-pasted into the text box. Then the user can add commentary and additional references. After the user adds commentary on the error and clicks submit the two text fields will be sent to two places â our database and a landing page where the accuracy flags will be delivered in real-time.
Moreover, the script would allow the user to see, if he/she desires which areas of the text are highly controversial and had many people commenting on them. This would be made by attributing hotter colors to more disputed/commented paragraphs and lighter colors to the others. This functionality is inspired by this tool developed for the purpose of revising the GPL licenses.
The text should disappear from the two boxes and instead be replaced by a popup dialog box that says âthank you for your contribution.â
Implementation
- 1. Name application
- 2. Reach out to Mozilla community to build proposed FireFox application extension.
- 3. Work with Wikimedia/Bridgespan to incorporate landing page and application with Wikipedia.
Discussion Questions
- How do we keep this tool from being an invitation to massively and scrupulously edit only topics like the Taylor Swift article?
- What should we name our application?
- Wiki Peer Review
- WikiNation; WikiWorld
- Our Wikipedia
- Wikipedia For Life (W4L)
- Compare the average discussion happening in a Wikipedia discussion page and one happening on a Youtube video. Which one is better?